Everything You Need to Know About Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
A guide to understanding VDI and how to choose the right solution
Summary
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) delivers secure, centralized desktop environments from a data center or cloud to any device. This guide explains how VDI works, why it’s gaining momentum, and how it compares to Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS).
You’ll discover:
- How VDI centralizes IT management while improving security and flexibility for hybrid work.
- Key differences between VDI and DaaS, and when each is the better choice.
- Common use cases across industries like healthcare, education, finance, and manufacturing.
- Best practices for selecting and deploying a scalable VDI solution.
Introduction
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a popular topic of conversation about remote work, hybrid IT, and secure application delivery. Organizations need to support remote and hybrid teams, protect sensitive corporate data, and manage increasing IT costs, like PC infrastructure. The answer for many organizations, ranging from schools, to government institutions and commercial companies, is VDI.
This guide will help you understand VDI. We'll explain how it works, its core benefits, how the common solutions compare, and how to choose the right solution for your organization.
What is VDI and How Does it Work?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure creates virtual workspace environments (comprised of a desktop operating system, applications, and data) that reside on a cloud data center server instead of on physical user devices like laptops.
Rather than installing an operating system (often Microsoft Windows) and individual applications on a physical PC, a desktop lives as an image on a server and is "streamed" to the user's endpoint device. The user's device (a laptop, thin client, or even a tablet) simply acts as a screen to display and interact with their server-delivered desktop, which is running securely in your data center or the cloud. All the data processing work also happens on the server, so no data resides on the actual device itself. In addition, the organization's IT department manages performance, security and all updates centrally, eliminating the need to interact directly with multiple physical PCs.
The result is a secure, self-contained virtual workspace environment that users can access from anywhere on any device. Some environments can even be accessed through a modern Web browser.
Most VDI Environments Typically Include:
- A Connection Broker or Session Manager that directs users to available desktops or apps.
- A Hypervisor layer that creates multiple virtual machines to host desktops. The most common hypervisors in use include VMware ESXi, Nutanix, PromoxVE, KVM, and VergeIO.
- Multiple desktop and application servers running mostly Windows or Linux workloads.
- One or more secure gateways that provide encrypted remote access without the need for a VPN.
- Individual endpoint clients that let users access desktops. Common examples include Macs and PCs, thin clients, tablets and Web browsers.
Thin clients are an increasingly popular choice that offers a low-cost alternative to conventional "fat" client laptops and desktops in school computer labs, and business that have shared workspaces like call centers and hospital nursing stations. A thin client uses a light-weight operating system that is managed centrally over the LAN and includes an embedded application that works with the VDI platform in use. One such example is Inuvika's ResoluteOS. The ResoluteOS thin client OS includes the embedded Inuvika Enterprise Client application, which provides optimal performance and stability for OVD users.
This architecture enables employees and students to access their digital workspace from anywhere, while IT retains full control.
Is App Virtualization the Same as VDI?
While the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a distinct difference between delivering a single virtualized application and delivering a full virtual desktop. The right choice for your organization depends entirely on your users' needs.
Application Virtualization Delivers Just the Tools
Application virtualization separates a specific application, or groups of applications, from the underlying operating system and delivers it to the user's device through some defined interface.
How it Works
Rather than streaming an entire desktop, the application runs on the data center server and the user accesses it in a few different ways:
A Stand-alone Window
The virtualized app appears on the user's local desktop, as if it were installed locally. Users can pin it to their taskbar and interact with it alongside their local apps. Inuvika OVD Enterprise refers to this feature as "App Mode."
A Web Portal
Users log in to a Web page that shows a menu of available applications. Clicking an icon launches the app and the user interacts with the app through the browser. The app windows generally behave as they do on regular desktops.
A Shared Desktop Session
Multiple users can log into a shared server desktop (like a Windows Remote Desktop Server), where they all have access to the same set of published applications based on their defined permissions. The desktop looks and feels like a local desktop, but runs on the server, not on the user's local device. The desktop is also locked down and cannot be personalized by the user.
The key takeaway is that the user isn't getting a dedicated operating system. They are only accessing specific tools, and the desktop acts as a simple interface for working with the app. This method is highly efficient for task workers who only need access to a few key applications to do their jobs, for example, shift workers who share workstations or student computer labs.
Full VDI Delivers the Complete Desktop Experience Through the LAN or Cloud
On the other side, full VDI delivers the entire desktop operating system (like Windows 10 or 11, or Linux) to the user, providing a complete desktop environment, complete with applications published according to the user's profile.
There are two primary ways to deliver these full virtual desktops:
Persistent Desktops
Each user is assigned a dedicated virtual desktop that they can personalize. Rather than installing the desktop on a laptop, it resides as an image on a data center server. When a user logs into a session, the desktop is "streamed" to the user's device. They can install their own applications, change the wallpaper, and save files directly to the desktop. All of these changes remain and are saved for their next session. This is ideal for workers who need a customized and consistent environment every time they log in.
Non-Persistent (Pooled) Desktops
This model uses a master generic image for a pool of users. When a user logs in, they are assigned a random desktop from the pool. They can use it for their session, but when they log out, the desktop is wiped clean and reset to its original state. This approach is highly secure and easy to manage, making it perfect for call centers, computer labs, and task workers where a standardized, non-personalized desktop is enough.
Modern platforms like Inuvika OVD Enterprise allows IT teams to do both, and deliver virtualized applications, persistent desktops, and non-persistent desktops all from a single installation to meet the diverse needs of a workforce.
The following summarizes the key differences:
Feature | Virtual Desktop Infrastructure | App Virtualization |
|---|---|---|
Primary Focus | Deliver a complete desktop, pre-populated with apps. | Deliver one or more applications without a desktop. |
User Experience | A complete, dedicated desktop environment. | Apps appear on local desktops or in a Web portal. |
Personalization | High (Persistent) or None (Non-Persistent). | None. Users access apps through a standardized interface. |
Resources Required | Higher. Each user has a dedicated desktop instance. | Lower. Multiple users share a server-based instance of Windows or Linux OS. |
Best For | Workers and power users who need a full and customized desktop. | Shared work environments, and users who need a few specific apps without a full desktop. |
Recommended Resources
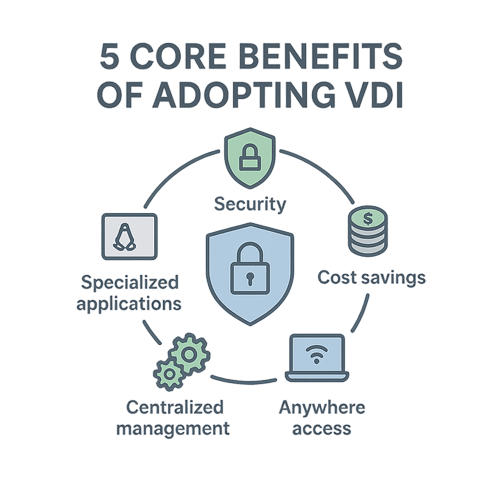
Five Core Benefits of VDI
Many organizations choose to implement a VDI solution to solve specific business challenges. Here are the most common advantages that organizations experience:
Enhanced Security
With VDI, your data never leaves the secure data center server. If an employee's laptop is lost or stolen, no sensitive corporate information is at risk because nothing is transmitted to or stored on the device itself. This has a significant impact on data protection and regulatory compliance efforts.
Reduced IT Costs and Complexity
Deploying virtual workspace environments with VDI eliminates the endless cycle of replacing obsolete PCs that can no longer support modern operating systems like Windows 11. In their place, you can deploy lower-cost, longer-lasting thin clients that now access modern desktops through VDI. They also have the added benefit of IT teams deploying, managing, and updating hundreds, or even thousands, of desktops from a single, central console instead of physically touching every individual machine.
Remote Access and BYOD
VDI enables your workforce to be productive from home, the office, or on the road. It also makes "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD) policies safer and easy to implement, as personal devices can securely access corporate resources without downloading data, managing problematic VPN connections, or allowing open LAN access that can lead to malware infections, and other security risks.
Centralized Management
Patching, application updates, and user onboarding become easier and more efficient. IT teams can deploy a new application to individual or even hundreds of users in minutes through centralized user preferences, ensuring everyone is running the same secure, up-to-date software. System health can also be monitored centrally, alerting administrators to potential problems ahead of time and allowing proactive troubleshooting.
Support Legacy Applications and Workloads
VDI is a powerful way to support legacy Windows applications or specialized Linux applications to any user, regardless of their own local operating system. Rather than dealing with the risks and implications of supporting an old version of an operating system, or application on physical devices, they can now be delivered virtually, along with the added benefits of improved security and stability.
Recommended Resources
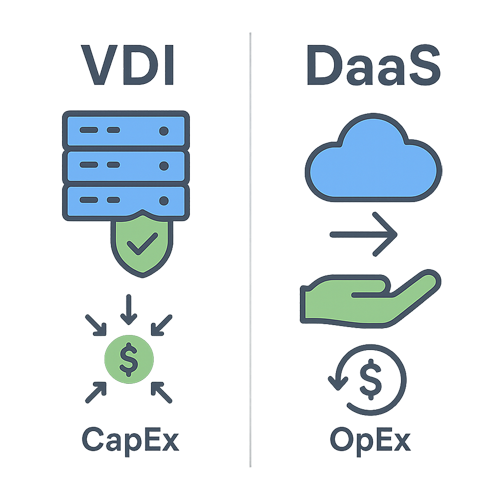
VDI vs. DaaS: What are the Key Differences?
Quite often, the term "Desktop-as-a-Service" is associated with VDI. While the two are related, they differ by one key element: who manages the VDI environment.
Feature | Virtual Desktop Infrastructure | DaaS (Desktop-as-a-Service) |
|---|---|---|
Hosting | Self-hosted on-premises, or in the organization's private cloud datacenter | A third-party service provider (MSP) hosts and manages it for organizations. Clients pay a reoccuring fee much like a utility. |
Control | Organizations have full control over the hardware, software, security, and day-to-day management of the VDI envrionment. | Less direct control. The service provider is typically responsible for managing the infrastructure (updates, etc.) while organizations manage the desktops, applications, and user preferences. The level of service can vary, however, based on services negotiated in a service level agreement. |
Cost Model | A mix of upfront capital expense (CapEx) for hardware and licensing. Some VDI software providers like Inuvika offer pricing in the form of 100% OpEx subscription plans. | Usually a predictable operating expense (OpEx) via a monthly or yearly subscription. |
Best For | Organizations that want maximum control, security and customization of their VDI environment. | Organizations with small IT teams, or want to outsource IT management and prefer an OpEx model. |
Inuvika Gives You Choice in How to Deploy VDI
Inuvika's flexible subscription model gives clients the best of both worlds. Organizations can deploy OVD Enterprise in their own data center (like other traditional VDI solutions) or work with one of our global hosting partners to access it as a fully managed DaaS solution.
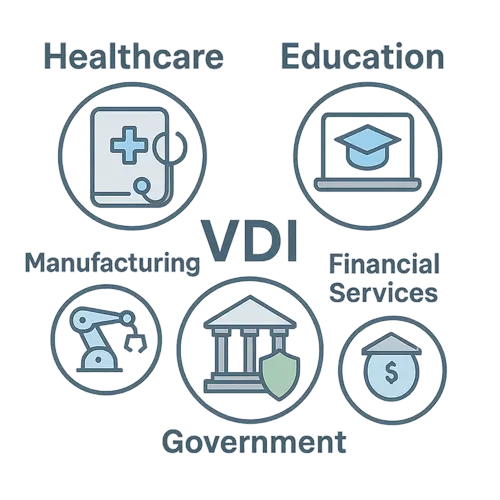
Who Uses VDI? (Common Industry Use Cases)
VDI can deliver strong value to clients in many different sectors, especially those that are subject to strict security and compliance standards related to data privacy and confidentiality.
Some common use cases for VDI include:
Healthcare
VDI enables healthcare professionals to securely access patient information (Electronic Health Records) from any shared workstation or tablet in a hospital or clinical setting, ensuring HIPAA compliance, improving clinical workflows, and accelerating patient care. About Inuvika in Healthcare
Education
Schools and universities can use VDI to provide students with access to specialized software and learning resources on any device, from campus computer labs to their own laptops at home. About Inuvika in Education
Government and Public Sector
Government agencies rely on VDI to meet stringent security standards, control access to sensitive information, and enable secure remote work for public sector employees. About Inuvika in Education
Manufacturing
VDI can be used on the factory floor and in the design office. It protects sensitive intellectual property, like designs and schematics, by keeping them on a central server instead of on vulnerable workstations or laptops. It also allows engineers to securely deliver powerful CAD/CAM design software to any device, and production managers to access ERP, CMMS, and MES applications from remote offices, ensuring uptime and access to critical production applications.
Financial Services
Like other highly-regulated industries, banks, investment firms, and insurance companies can use VDI to secure access to sensitive client financial data and meet strict regulatory standards like SOX and others. It enables secure remote trading and allows financial advisors to access client information from distributed branch locations without risking data confidentiality, since no information is ever stored on the local device.
Managed Service Providers
VDI enables MSPs to transform their business model to high-margin managed services by using a multi-tenant VDI platform to host and manage their clients' entire desktop environments in their own data center or private cloud.
And Many Other Industries
VDI offers value to nearly every industry. Retailers use it to deploy point-of-sale systems, law firms use it to secure confidential client case files, and call centers use it to provide agents with standardized and secure access to customer relationship management (CRM) tools, whether they are in the office or working from home.
Recommended Resources
How to Choose the Right VDI Solution Provider for Your Industry
CMMC Compliance and Virtual Workspaces for Defense Contractors
Why Linux Virtualization Software Is Gaining Momentum in Education and Research
Inuvika Named Best Virtual Classroom Software by Research.com
Case Study: Inuvika Powers Virtualized Applications for Genomics England
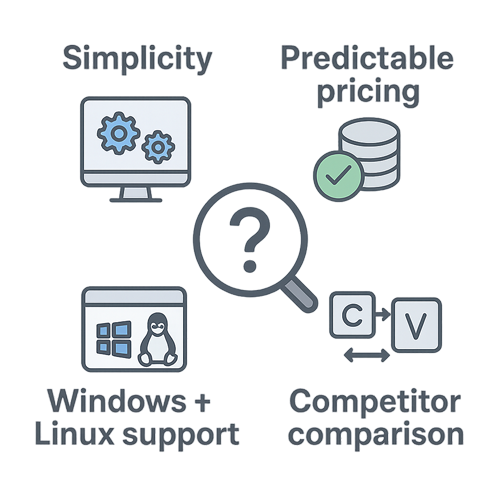
How to Choose the Right VDI Solution
There are many competing VDI solutions in the marketplace today, but not all are created equal. As the cost of traditional vendor offerings like Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops and Omnissa Horizon (formerly VMware Horizon) continues to rise, customers are increasingly turning to alternatives like OVD Enterprise to modernize and reduce the cost of their VDI strategy.
As you evaluate your own options, consider the following factors:
How complex is the deployment and management?
Will you need a team of certified specialists and weeks of professional services?
Is the pricing model simple and predictable?
Or are there hidden costs for essential features like load balancing and reporting?
Does it support both Windows and Linux applications?
Can you manage both from a single platform?
How does it compare to the traditional and legacy solution providers?
Is it a viable, more cost-effective alternative to solutions like Citrix or VMware?
Recommended Resources
Seven Challenges to Citrix Workspace and How Alternatives Can Help
Ten Reasons to Consider a Citrix Alternative For Your Business
Why It's Time to Rethink Your VDI Stack
What Makes an Efficient Virtual Desktop Environment?
Case Study: Canadian Health Systems Delivers Apps-as-a-Service to Medical Clinics
Inuvika OVD Enterprise is VDI Simplified
For organizations that find traditional VDI solutions too costly and complex, Inuvika OVD Enterprise is the answer. OVD is a simple, secure, and incredibly cost-effective VDI platform that delivers virtualized desktops and apps for up to 60% less than competing solutions.
OVD Enterprise offers:
Integration & Simplicity
OVD deploys quickly with a single, easy-to-use admin console for fast deployment and management
Predictable, All-Inclusive Pricing
One concurrent user subscription fee with no hidden costs or surprises.
Unmatched Flexibility
Natively deliver both Windows and Linux apps and desktops from the same platform as a Service, or on-premises.
Proven Security
Advanced security for reliable remote access without the need for a VPN.
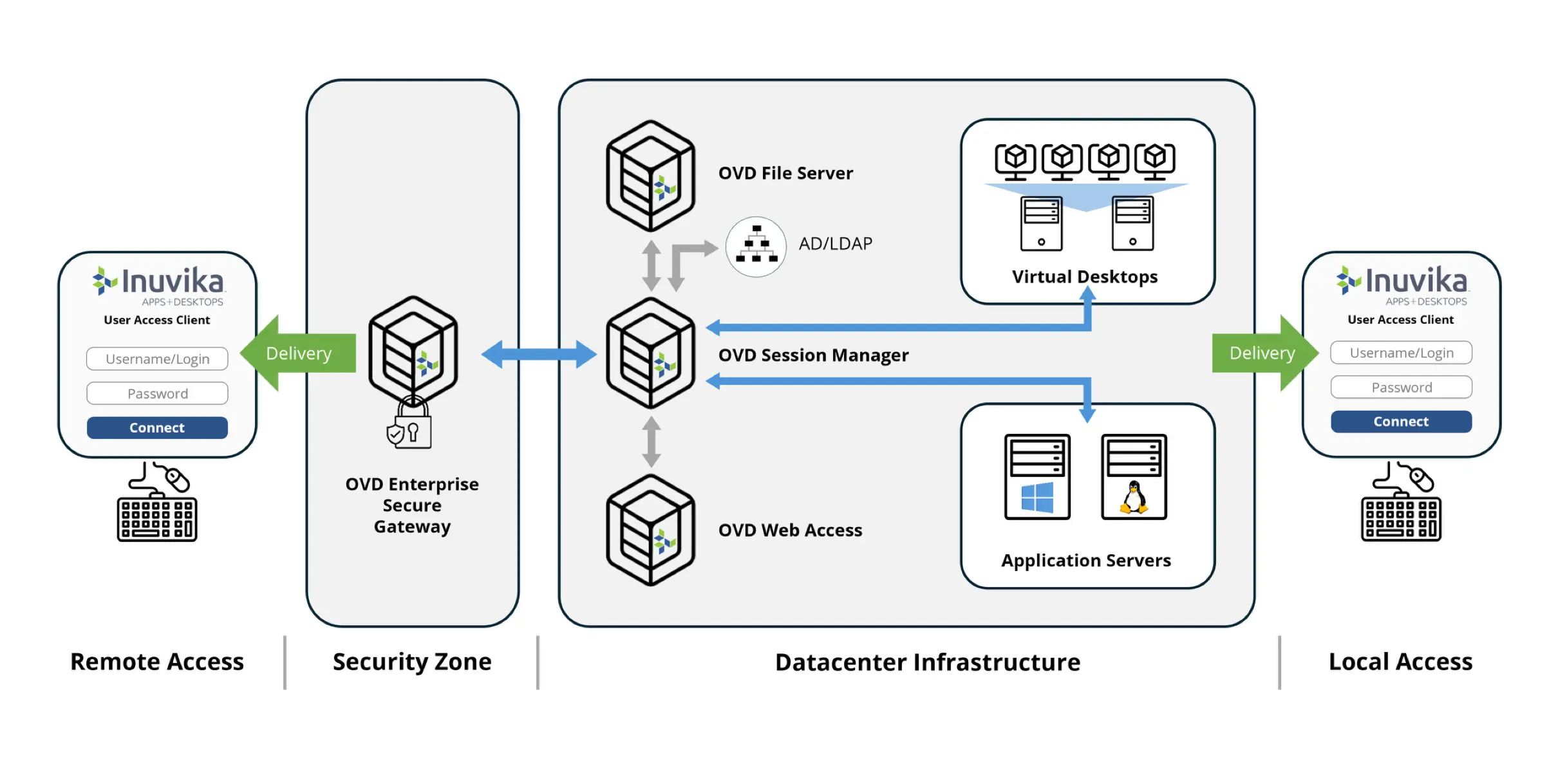
How OVD Enterprise Works
OVD Enterprise is a modern, high performance platform architected to be less complex and more efficient than other solutions. OVD works with all leading hypervisor and cloud platforms, and can be deployed on-premise within your own cloud datacenter, or delivered as-a-service through one of Inuvika's hosting partners.
OVD Enterprise Architecture (Click to Enlarge)
Recommended Resources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)?
VDI is a technology that delivers desktop operating systems and applications from centralized servers to end users over a network. Instead of running locally, the virtual desktop runs in a data center or cloud environment, and users connect through thin clients, laptops, or Web browsers.
How does VDI work?
VDI hosts multiple virtual machines on a hypervisor within a central datacenter or cloud server. Each virtual desktop runs its own operating system instance. When users log in, they access this remote environment via a secure connection, receiving only screen updates while their inputs are sent back to the server. All processing of data resides on the server, so no data ever resides on the user's local device.
What are the main benefits of VDI?
VDI improves security, manageability, and scalability. IT teams can centrally deploy updates and enforce user policies, while end users gain secure access from any location or device without having to manage issues like downloading applications. It also reduces endpoint hardware costs and supports bring-your-own-device (BYOD) initiatives.
How is VDI different from Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS)?
While both VDI and DaaS deliver virtual desktops, VDI is typically self-managed within an organization’s data center or private cloud, providing greater control and customization. DaaS is hosted and managed by a third-party provider, offering simplicity and lower maintenance.
What types of organizations use VDI?
VDI is used across many industries, but is particularly well-suited to industries where data security, regulatory compliance, remote access, and centralized management are priorities, including healthcare, education, finance, and government/public sector. Each benefits from standardized user environments and controlled access to sensitive data.
What are the main challenges of implementing VDI?
The biggest challenges include infrastructure costs, storage performance, and ensuring a consistent user experience under network load. Proper sizing, user profiling, and GPU acceleration can help address these performance bottlenecks. Modern solutions like Inuvika's OVD Enterprise address many of these issues that often impact legacy solution vendors, and offer significant benefits while reducing costs.
How can VDI support hybrid and remote work?
VDI allows employees to securely access corporate desktops and applications from home or while traveling, without the need for using VPNs. By hosting complete desktop environments in the cloud or data center, organizations can maintain compliance and security while supporting a flexible, distributed workforce.
How does Inuvika’s OVD Enterprise fit into the VDI landscape?
Inuvika OVD Enterprise delivers the benefits of traditional VDI (centralized management, data security, and multi-device access) with a simplified architecture that reduces complexity and infrastructure costs. It’s ideal for organizations seeking an easier, more cost-effective pathway to virtual desktop and application delivery.
Next Steps

Ready to see a simpler way to VDI?